Unleashing the Potential: Hydraulic Drive Systems in Modern Industries
Introduction
Hydraulic drive systems, renowned for their high torque and exceptional control capabilities, continue to be integral to the evolution of machinery across various industries. From renewable energy to advanced aerospace applications, these systems offer unparalleled efficiency and versatility. As we look to the future, the role of hydraulic technology is not only expanding but also becoming pivotal in pioneering sustainable and innovative solutions.
What is a Hydraulic Drive Train?
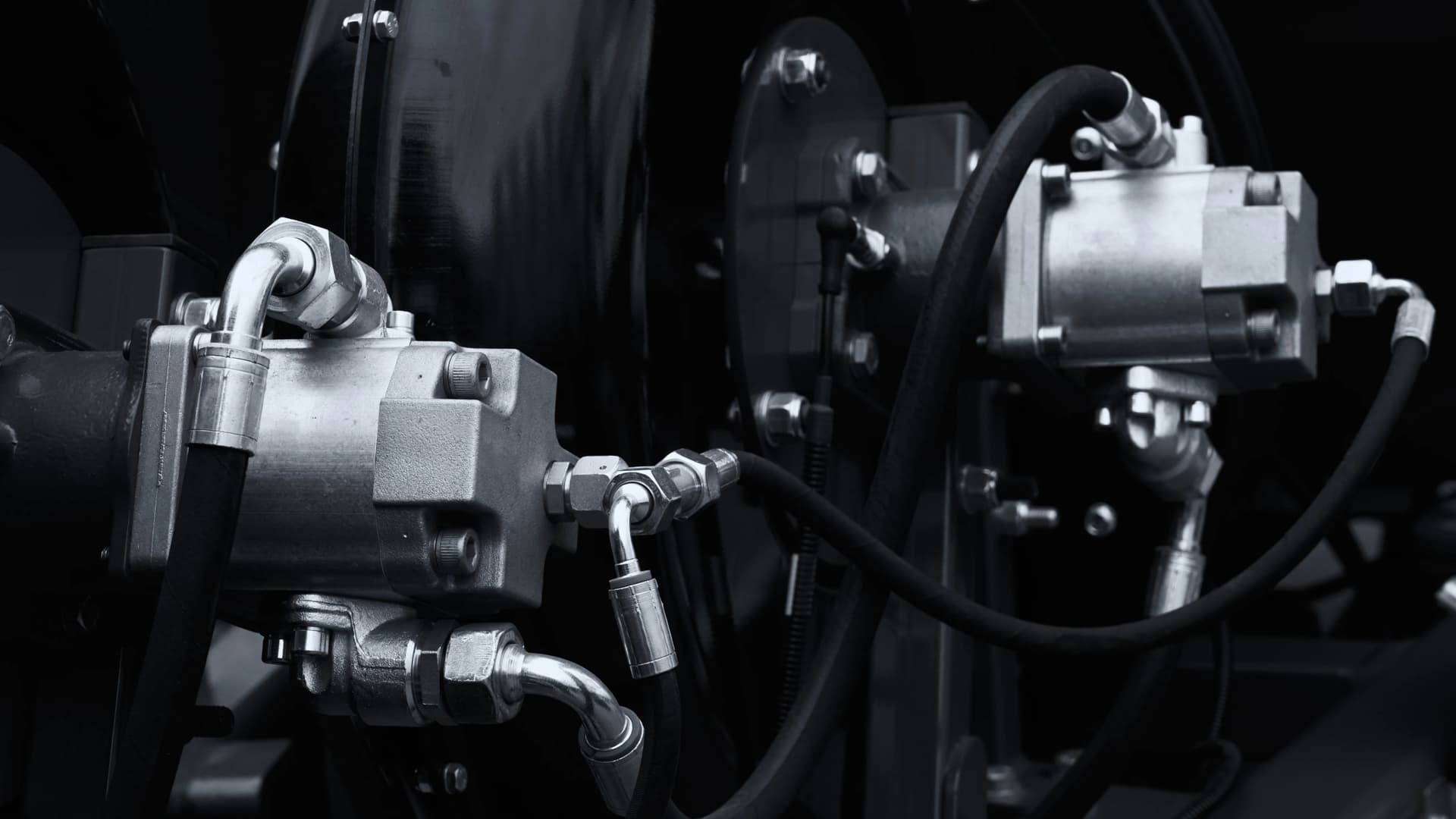
A hydraulic drive train consists of components that transmit power using fluids under pressure. Central to the system are the hydraulic pump and motor. The pump converts mechanical power from an engine or electric motor into hydraulic energy by pressurizing fluid. This fluid then flows through the system to a hydraulic motor, converting the hydraulic energy back into mechanical power to drive machinery. The process is controlled by valves that regulate the flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid, allowing precise control of the speed and torque of the output.
Comparing Drive Trains: Hydraulic vs. Mechanical vs. Electric
Mechanical drive trains typically use gears, belts, and chains to transmit power, which can be less efficient at low speeds and less flexible in terms of configuration. Electric drive trains use electric motors and often involve batteries or other electrical storage. They are known for their efficiency and cleanliness but can be limited in terms of torque output and are generally less robust under heavy load conditions compared to hydraulic systems.
Hydraulic drive trains offer several distinct advantages:
High Torque at Low Speed: Unlike electric motors, hydraulic systems can deliver high torque at very low speeds, which is crucial for applications like construction equipment and heavy lifting.
Flexibility in Configuration: Hydraulic components can be positioned flexibly within a system, connected by hoses rather than rigid mechanical linkages.
Modular and Scalable: Components can be added or reconfigured based on changing needs without redesigning the entire system.
Robustness and Durability: Hydraulic systems are typically more durable and better suited to harsh environments, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Renewable Energy Applications
In the renewable energy sector, hydraulic systems play a critical role in harnessing the power of natural elements. Wave and tidal energy projects greatly benefit from the robust and efficient nature of hydraulic technologies, which adeptly convert the kinetic energy of water into usable electrical power. These applications demand systems that can withstand variable and harsh conditions while maintaining high efficiency.
Construction and Mining Equipment
Heavy-duty machinery such as excavators and drills rely on hydraulic drive systems for their high torque output and precise control, essential in construction and mining operations. The future points towards smarter, more integrated hydraulic systems that enhance operational efficiency and reduce environmental impacts through improved fuel efficiency and emissions control.
Agricultural Machinery
In agriculture, the precision and adaptability of hydraulic systems facilitate advancements in automated machinery for planting, irrigation, and harvesting. These systems are set to become more interconnected, leveraging IoT technology for smarter farming solutions that optimize resource use and crop yields.
Automotive and Transportation
Hydraulic hybrid systems are gaining traction in the commercial transportation sector, especially in urban heavy vehicles like buses and trucks. These systems are ideal for stop-start conditions common in urban settings, storing energy in hydraulic accumulators to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.

A notable innovation in hydraulic applications is the development of the Flowcopter, a hydraulic-powered drone. Unlike traditional drones that rely on electric motors, the Flowcopter utilizes hydraulic motors and pumps to achieve significantly greater endurance and payload capabilities. This unique application of hydraulic technology enables the Flowcopter to operate in environments and for durations that electric drones cannot match, opening new possibilities for uses in remote or harsh conditions.

Conclusion
As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, hydraulic drive systems are increasingly recognized not just for their traditional benefits but also for their potential in driving innovation. With advancements in technology and integration capabilities, hydraulic systems are set to revolutionize industries by providing solutions that are not only efficient but also adaptable to the changing environmental and technological landscapes. As we move forward, the versatility and robustness of hydraulic technology will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a sustainable and efficient future for industrial applications worldwide.